Blue Light Blocking Lenses Carried by Laramy-K Optical Lab
On this page you'll find a guide to the blue light blocking lenses offered by Laramy-K Optical Lab. You'll find details on each lens option, including the specific wavelengths they block, along with explanations of blue light, visible light, and other related information, so you can understand how these lenses work.
VisionEase Poly Clear Blue
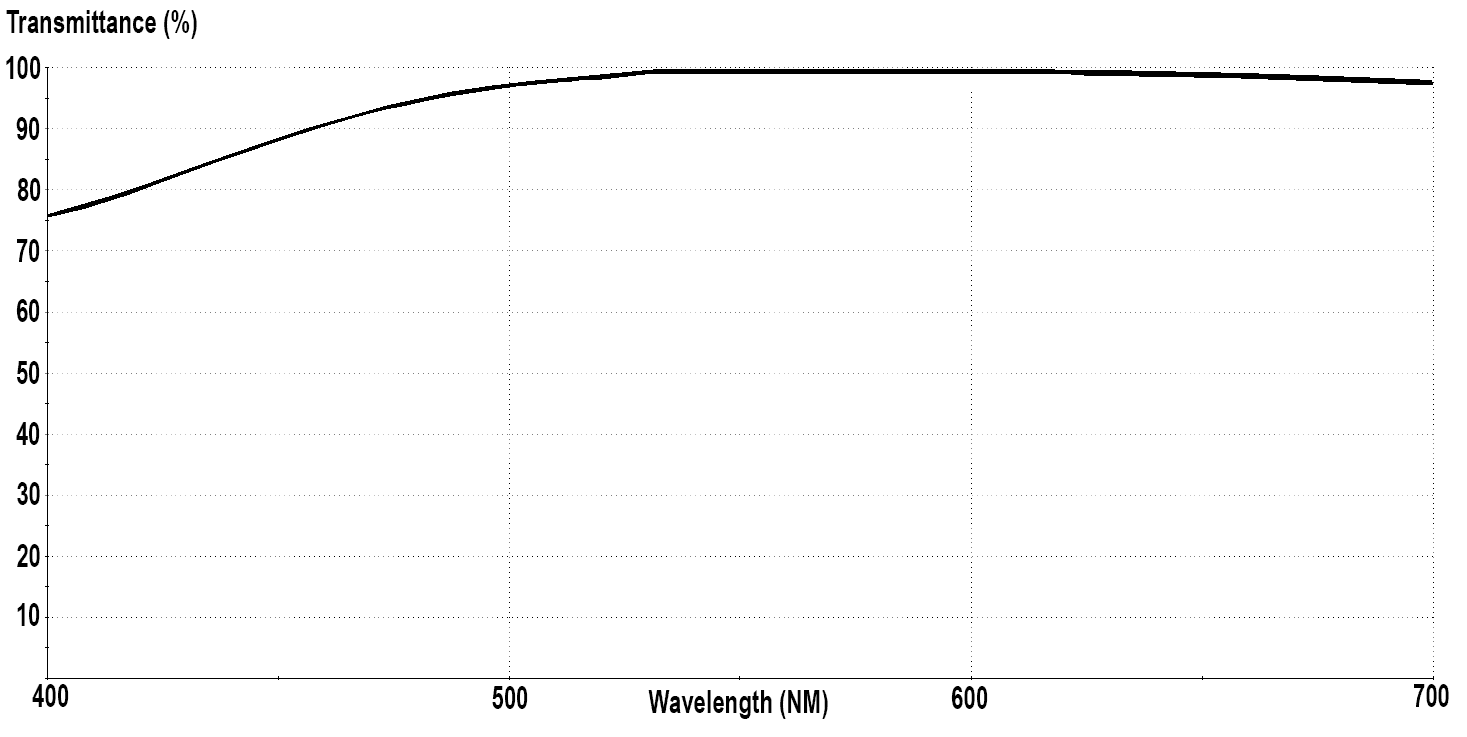
The VisionEase Clear Blue lens blocks 100% of UV radiation up to 400nm and 67% of short-wavelength blue light between 400-425nm to offer protection against HEV light. The Vision Ease Clear Blue lens has earned the Skin Cancer Foundation’s seal of recommendation. The lens absorbs violet and blue wavelengths, reducing glare and contrast loss caused by blue light scatter.

Conant CR-39 UV++
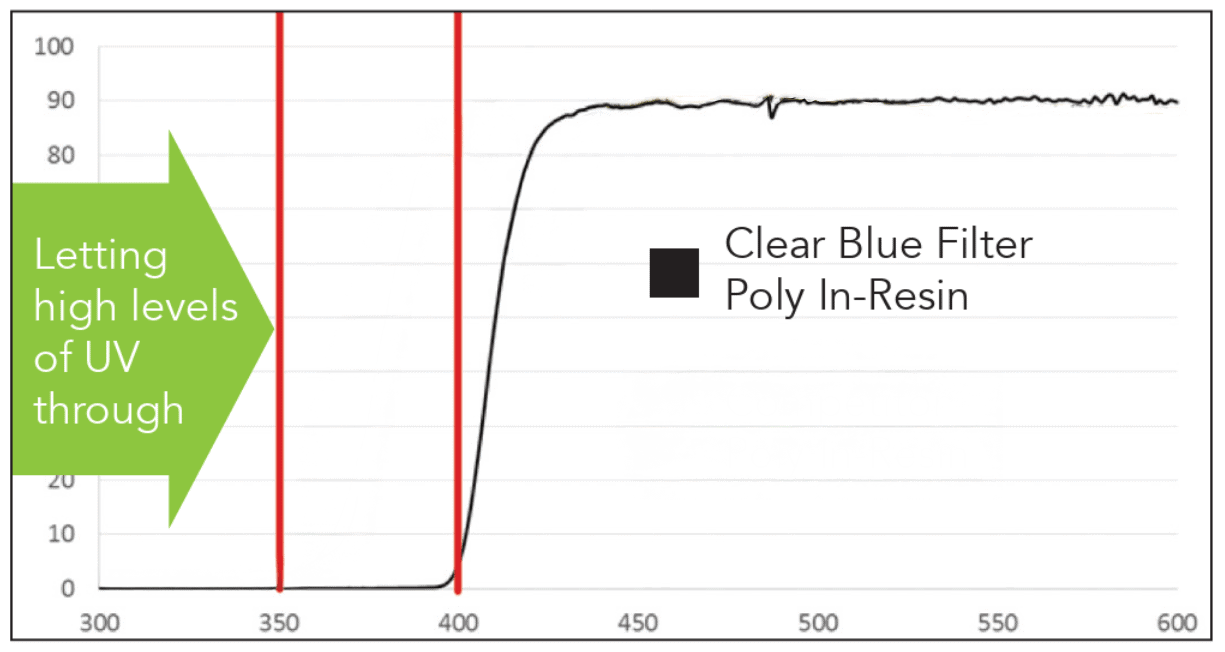
The Conant CR-39 UV++ lens provides 100% UV400 protection while filtering HEV blue light between 400-420nm. Maintaining an Abbe value of 58 to ensure superior optical clarity and reduced chromatic aberration. The UV++ technology aims to reduce digital eye strain and retinal stress while protecting from harmful UV light.

Younger 1.66 UV 420
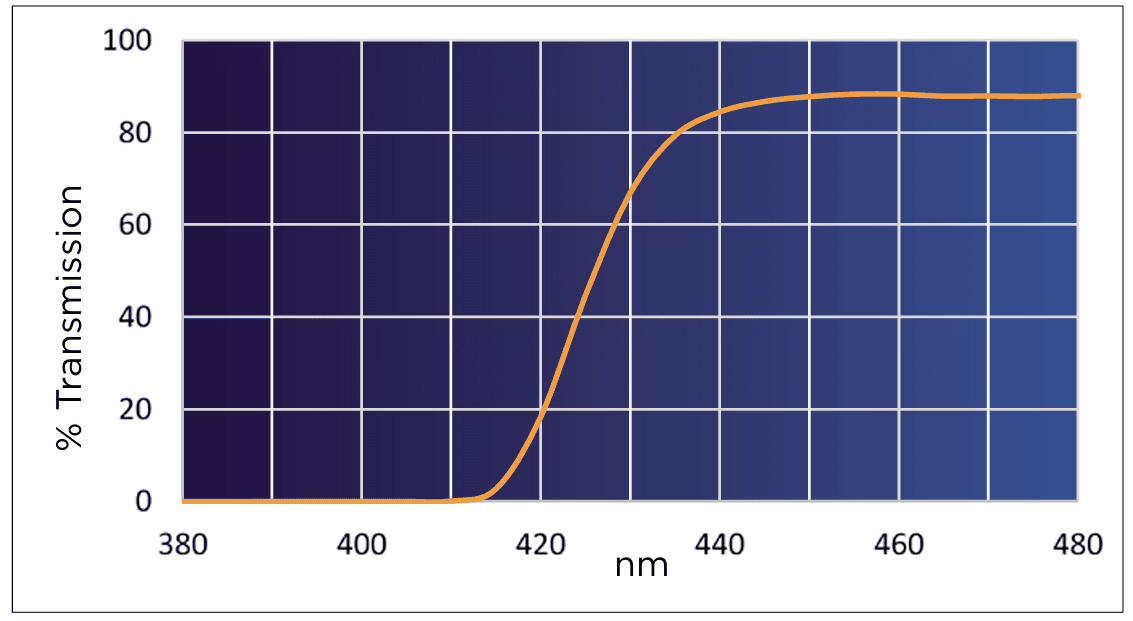
The Younger 1.66 UV420 lens provides 100% protection against UVA and UVB rays while filtering 80% of HEV blue light at 420nm. This lens offers effective blue light reduction without a visible tint.

Shamir Trivex Blue Zero
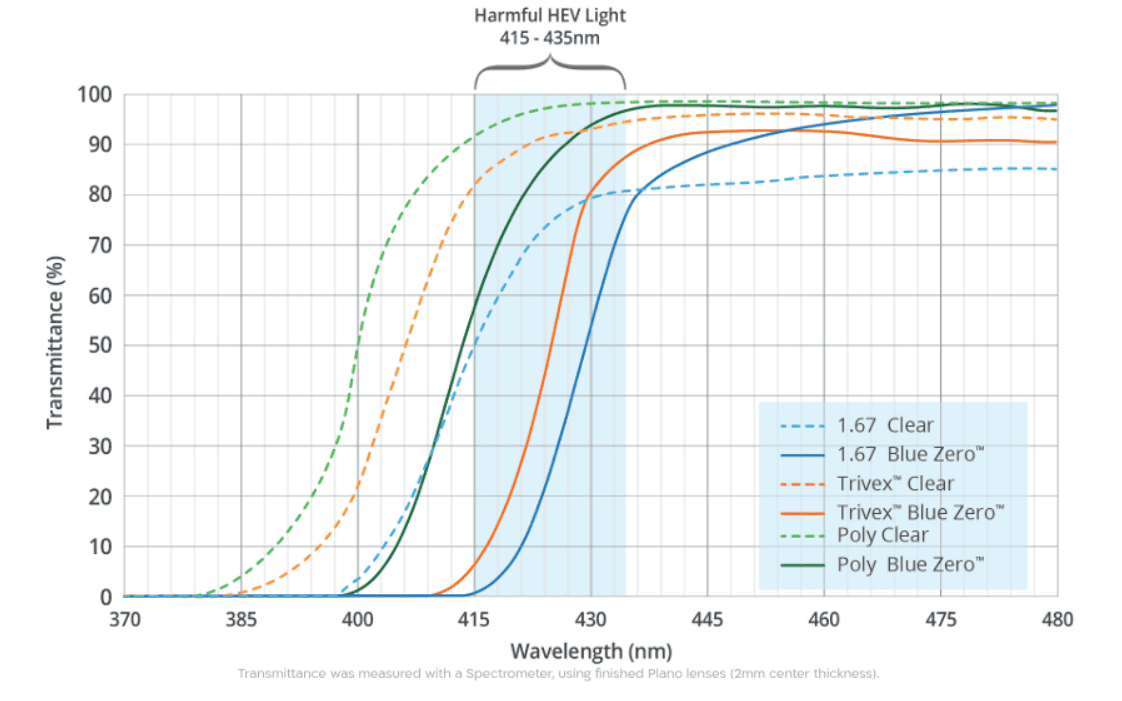
The Shamir Trivex Blue Zero lens is designed to provide blue light protection while maintaining high visual clarity and contrast sensitivity. The lens effectively blocks up to 98% of HEV blue light in the 415-435nm range without distorting natural color perception. Unlike coatings or tints, Blue Zero is built into the lens material itself. Additionally, the lens offers full UV protection.
BluTech Poly Indoor
BluTech CR-39 Indoor

BluTech 1.56 Indoor

BlueTech Poly Polarized Outdoor

BluTech 1.56 Bifocal Flat Top 28 Outdoor

BluTech Poly BluLite 430 Everyday
BluTech CR-39 Everyday BluLite 430

BluTech 1.66 BlueLite 430 Evening
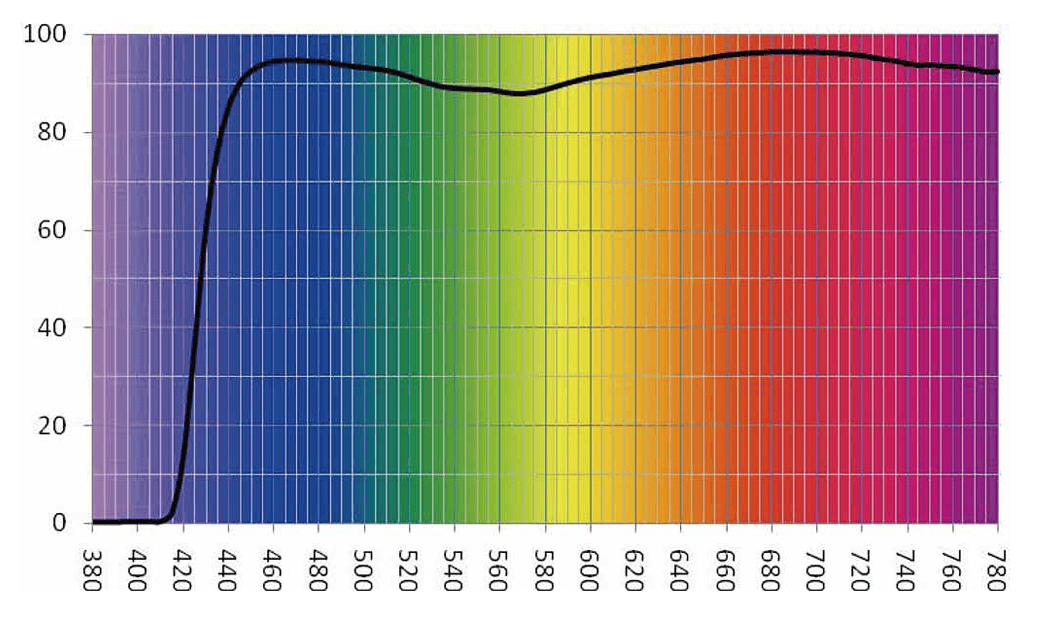
BluTech lenses filter HEV blue light in the range of 400 to 455 nanometers. By infusing ocular lens pigment and melanin directly into the lens material, BluTech effectively mimics the eye's natural protective mechanisms, offering enhanced contrast, reduced glare, and improved visual acuity without distorting color perception. Available in both indoor and outdoor options, BluTech lenses also provide protection from harmful UV light.
About Blue Light Lenses
Blue light is part of the visible light spectrum, falling within the range of 400 to 500 nanometers. Natural sunlight contains blue light, but artificial sources such as LED lights, fluorescent bulbs, and digital screens also emit significant amounts of it.
How Blue Light Blocking Lenses Work
Blue light blocking lenses are designed to filter out a portion of blue light before it reaches the eyes. They use special coatings or lens materials that absorb or reflect blue light, reducing exposure. Some lenses have a noticeable yellow or amber tint, while others use nearly clear coatings that reflect blue light off the surface.
The effectiveness of blue light lenses varies from person to person, some people experience reduced digital eye strain and improved comfort. Some users have less fatigue and better sleep after wearing them, though there is no concrete evidence to support this. Digital eye strain is likely caused by prolonged screen use rather than blue light itself.
Blue Light Lenses as a Comfort Option
For those who experience screen fatigue or discomfort, blue light lenses may be worth trying. While they are not a guaranteed solution for digital eye strain, they might help reduce glare and improve comfort. More effective ways to minimize eye strain include taking regular breaks, adjusting screen brightness, and maintaining an appropriate viewing distance. Most devices also have a blue light filter setting that can be turned on.
The Different Wavelengths of Light
Light is made up of electromagnetic waves, and the portion visible to the human eye ranges from approximately 380 to 700 nanometers (nm).
Ultraviolet Light (100–400 nm)
- UVC (100–280 nm): The most energetic and potentially harmful form of UV light. Fortunately, it is almost entirely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere.
- UVB (280–315 nm): Partially absorbed by the atmosphere but still reaches the surface. Long-term exposure can contribute to cataracts and other eye damage.
- UVA (315–400 nm): Less energetic than UVB but penetrates deeper into the eye, potentially leading to macular degeneration over time.
Most sunglasses come with 100% UV coatings blocking all UVA and UVB light to protect your eyes.
Violet Light (380–450 nm)
- The shortest wavelength of visible light, sitting closest to UV on the spectrum. Violet and blue light play a role in maintaining circadian rhythms.
Blue Light (450–495 nm)
- Blue-Violet (380–450 nm): Contains the highest energy within the visible spectrum. It is most associated with potential digital eye strain.
- Blue-Turquoise (450–495 nm): Beneficial for regulating sleep-wake cycles by influencing melatonin production. Natural exposure to this wavelength from sunlight is important for overall health.
Cyan Light (495–520 nm)
- A blend of blue and green, contributing to color perception. Less studied than blue light but plays a role in overall contrast sensitivity.
Green Light (520–565 nm)
- Perceived as one of the most comfortable colors for the human eye. Helps with high-contrast visibility and is often used in optical coatings to reduce glare. Some research suggests green light therapy may help with migraines and eye strain.
Yellow Light (565–590 nm)
- Yellow-tinted lenses are used to filter blue light and reduce glare, especially in sports.
Orange Light (590–620 nm)
- Less intense than red but still beneficial for contrast and visibility. Often used in specialized eyewear to filter out blue light for better sleep regulation.
Red Light (620–700 nm)
-
- Red light has the longest wavelength within the visible spectrum and is the least energetic.
Laramy-K DES Coating
Laramy-K's DES coating helps filter high-energy blue light from screens and artificial lighting. It minimizes reflections on both the front and back of the lens, improving visual comfort during extended screen use. With a subtle blue hue, the coating reduces the amount of blue light that reaches the eyes while maintaining a clean, natural look.